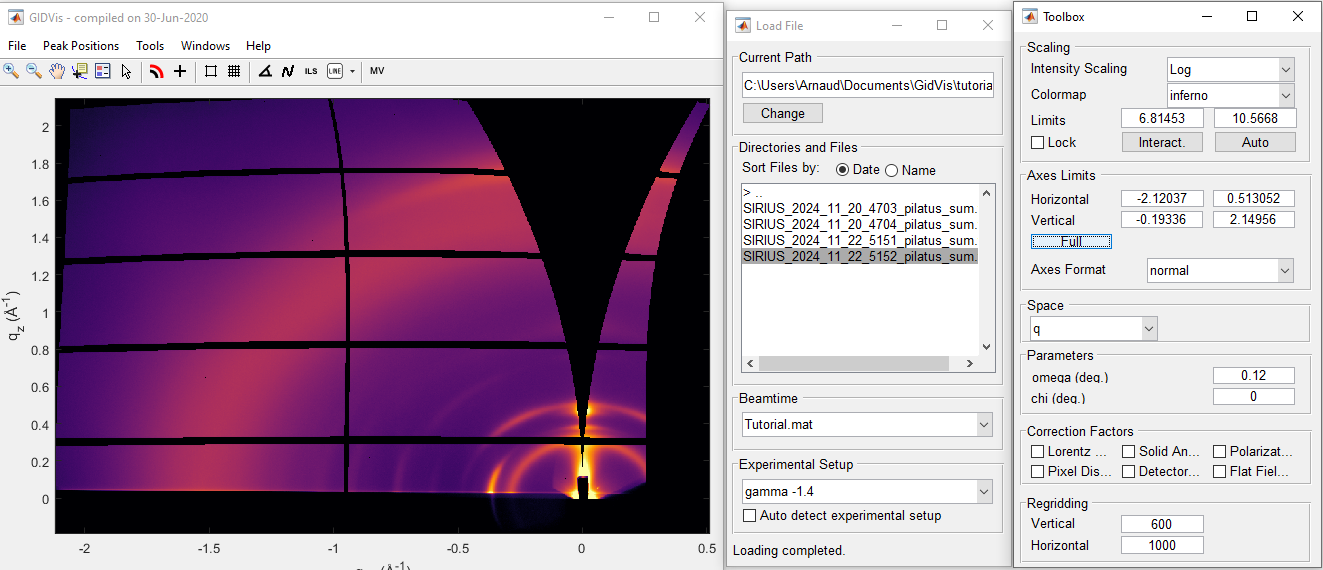
Convert to q space#
Select the file 5151 from the file list. This file was acquired at an angle of \({\rm gamma} = -0.75\) degrees. Choose the correct Beamtime (e.g., Tutorial.mat) and the corresponding Experimental Setup (e.g., gamma -0.75).
Configure the Toolbox window#
In the
Toolboxwindow, select the entryqin theSpaceframe.Click the
Fullbutton to automatically rescale the x and y axes.Change the
Intensity ScalingtoLog.
In the Parameters frame, enter the angle of incidence (referred to as \(\rm thetai\) in the notebook) in the field labeled omega. For this file, input the value \(0.12\).
You may notice thin black lines appearing on the image when switching to q space. To remove these lines without affecting the image quality, adjust the Horizontal parameter in the Regridding frame. A value of 1000 works well for this dataset. Your result should resemble the following:
Note on the correction factors#
GIDVis provides various correction factors. If you wish to apply them, refer to the GIDVis manual and ensure you fully understand the physical meaning of each factor. Generally, if you are not comparing peak intensities but focusing solely on peak positions, these corrections are unnecessary.
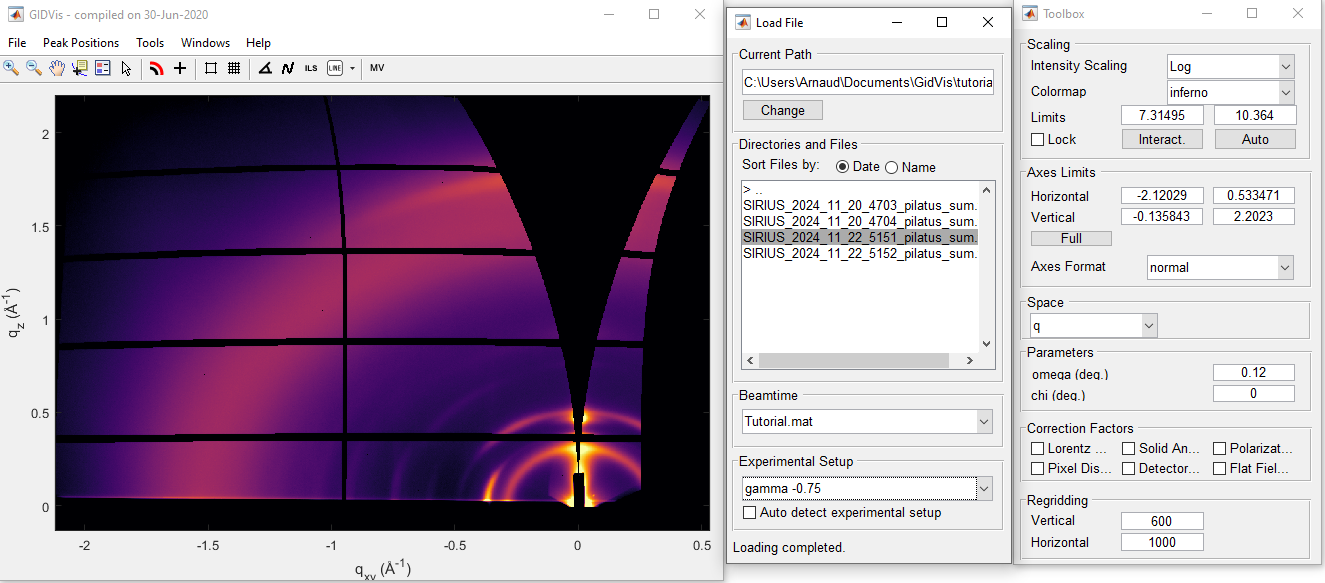
Change the experimental setup for each file#
For file 5152, acquired on the same sample but at an out-of-plane angle of \({\rm gamma} = -1.4\) degrees, you need to use the appropriate Experimental Setup.
In the
Load Filewindow, click on the scan5152.Select the
Experimental Setupnamedgamma -1.4.In the
Toolboxwindow, clickFullto rescale the axes.
The processed result should look like this: